Conversational AI is all around you.
There are obvious examples like Siri, Alexa, in-car voice systems, or chatbots on your favourite ecommerce website.
But you’ve probably also used AI to generate live transcripts of work calls or give feedback to your HR lady. You might even have some smart appliances at home that tell you when there’s an error.
So, let’s go more in-depth here and see conversational AI examples that do more than everyday convenience and actually help your business grow.
Discover how conversational AI really works with Lyro
What is conversational AI and how does it work?
Conversational AI is a type of artificial intelligence that enables computers to understand and respond to human language in a natural way. It powers chatbots, virtual assistants, and voice-enabled applications, allowing them to interact with people using text or speech.
So, how does it actually work?
At its core, conversational AI works through a combination of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning. The system receives a user’s input, either as text or speech, and breaks it down to understand intent as well as key information. Then, machine learning models determine the best response or action, which results in the system generating a natural-sounding reply to the user.
It’s good to note that AI learns and improves over time. So, the more it interacts, the more it can learn from patterns and context, making conversations smoother and more personalized.
Key components of conversational AI
Conversational AI may feel like a human when you’re chatting with it, but behind the scenes, it relies on several powerful components working together. Each element plays a unique role in helping machines understand human language and respond in a way that feels.
Let’s break down the main components that bring these intelligent interactions to life:
- Machine learning: helps the system improve over time. It analyzes large sets of conversations and interactions to detect patterns and predict outcomes.
- Natural language processing (NLP): allows machines to understand and interpret human language. It breaks down text or speech into smaller pieces so the system can figure out what the user is really asking.
- Language models: AI systems trained on massive amounts of text data to generate human-like responses. They learn the structure, tone, and flow of human language to produce answers that feel natural and coherent.
- Sentiment analysis: helps conversational AI detect the emotional tone behind a user’s words. By analyzing the phrasing and punctuation, the system can tell whether someone is frustrated, happy, or confused.
- Entity recognition: identifies and extracts specific details from a user’s input. These entities can be names, dates, product IDs, locations, or any other key pieces of information relevant to the conversation.
Read more: Discover the key differences between chatbots and conversational AI.
Conversational AI examples
Conversational AI isn’t limited to one industry or use case. It’s a technology that adapts to countless scenarios where people need quick and intuitive interaction. From ordering a pizza with your voice to resolving IT issues in seconds, AI-powered systems help businesses communicate with customers better. Here are some real-life conversational AI examples:
Virtual assistants
Virtual assistants are AI-powered systems designed to help users complete tasks and answer questions through voice or text. They offer hands-free interaction as well as integrate with apps and services. Think of Siri on your phone. That’s a virtual assistant.
Common tasks include scheduling meetings, checking the weather, controlling smart devices, and setting up your alarm. You name it. Their main goal is to make everyday tasks more convenient.
A leading platform for virtual assistants is Amazon Alexa, which integrates conversational AI into smart speakers and other devices. Another notable example is Google Assistant, which is widely available on smartphones and smart home systems.

An example of a business using virtual assistants is Domino’s Pizza. This company uses Amazon Alexa to allow customers to place orders with a voice command. This makes ordering faster and enhances customer experience.
Customer service chatbots
Customer service chatbots are conversational AI tools that handle customer inquiries in real time. They are available 24/7 and can manage high volumes of repetitive requests without human intervention. By automating simple tasks, they reduce wait times and free up human agents to focus on more complex or sensitive issues.
A popular platform for building customer service chatbots is Tidio, which helps businesses deliver seamless support across multiple channels. And for more flexibility, the platform also provides live chat, chat flows, and a help desk system.
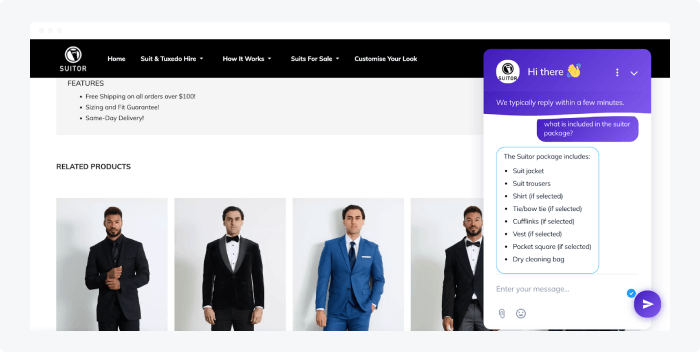
An Australian suit and tuxedo rental company, Suitor, uses Tidio AI to offer 24/7 customer service and automate processes such as answering frequently asked questions and sorting through requests. Since implementing Tidio, the business has achieved 85% support automation and decreased waiting times by 97%.
The number one thing that has grown our business is offering that customer service experience the rest of the market has not been able to do.

Call center agents
AI-powered call center agents assist human representatives by handling routine calls and providing scripted responses. Unlike traditional phone systems, conversational AI agents can understand natural speech, route calls intelligently, and even analyze customer sentiment in real time.
In hybrid setups, AI handles common issues, while human agents step in for complex cases. This reduces call waiting times while improving consistency and customer satisfaction.
One of the leading platforms for AI call center solutions is Five9, which integrates conversational AI into inbound and outbound calls. Another major player is Genesys Cloud CX, offering AI-powered voicebots that can scale across global customer service operations.
Microsoft used conversational AI to revamp its massive global call center operations, saving $500 million in one year. By unifying its systems under Dynamics 365 Customer Service and integrating AI-powered tools like Copilot, Microsoft automated time-intensive tasks such as case summarization, response generation, and knowledge search.
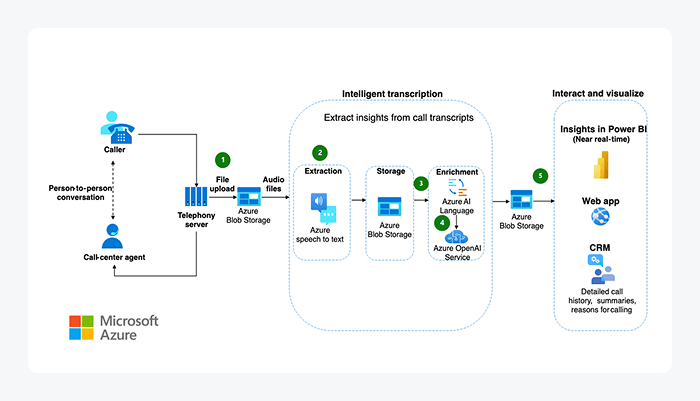
These capabilities enabled faster resolutions and better routing, while also helping agents onboard quicker and handle more cases.
Sales assistants
Conversational AI sales assistants are designed to guide potential customers through the buying journey. They can qualify leads, recommend products, answer pre-purchase questions, and even upsell or cross-sell based on customer behavior.
Unlike generic chatbots, AI sales assistants use personalization and intent recognition to engage users in a way that mimics a real sales rep. This creates a smoother shopping experience and helps businesses increase conversions without scaling their sales teams.
A well-known platform for AI-driven sales assistants is Drift, which focuses on conversational marketing and sales automation. Another strong option is Tidio, which combines AI-powered chat with ecommerce integrations to help businesses boost sales directly on their websites. On top of sales, Tidio also helps your support team boost efficiency and automate your customer service inquiries.
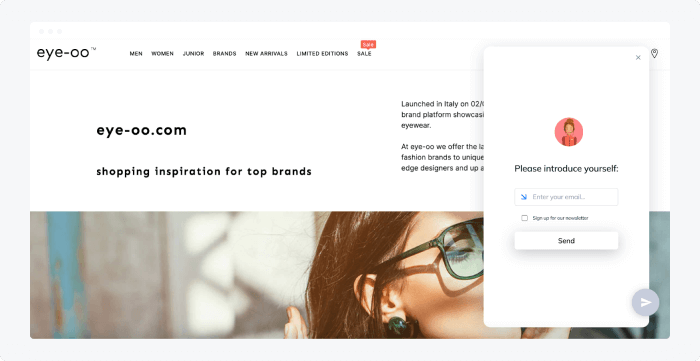
A multi-brand eyewear platform, eye-oo, used Tidio to interact with customers in real-time and boost engagement. And, as a result, the brand increased revenue by €177K and boosted sales by 25%.
Overall, Tidio exceeded our expectations! We knew that it had a variety of features to choose from, but did not know how powerful and effective they could be. Tidio has helped us with closing sales, building trust, and quantifying the impact of customer service.

Marketing automations
Conversational AI in marketing automation focuses on creating personalized, real-time customer engagement. Instead of generic email blasts or ads, AI-driven assistants can interact with prospects through chat to qualify and then nurture them with tailored content.
They can also segment audiences based on behavior and send messages at the right time. On top of that, you can set them to trigger campaigns automatically. This makes marketing more dynamic and responsive, helping businesses move leads smoothly down the funnel.
A popular platform for conversational marketing automation is HubSpot, which integrates AI chatbots into its marketing suite to engage and nurture prospects automatically.

For example, Mountain Dew launched DEWBot, their marketing chatbot. The company used this software to boost brand advocacy and engagement during its eight-week “Rig Up” campaign on Twitch. The bot was also nominated for the prestigious Shorty Award.
HR automations
Conversational AI in HR automations helps streamline repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as answering employee FAQs or guiding staff through company policies. Moreover, these automations can help with the hiring process as they can schedule interviews, do the initial screening, and then onboard the new hires.
Instead of sending multiple emails or filling out forms, employees can simply chat with an AI assistant to get instant answers or complete HR processes. This reduces the workload for HR teams while also improving employee experience by providing 24/7 support.
A well-known platform for HR automation with conversational AI is Paradox. The platform offers Olivia, an AI assistant for recruiting and HR tasks. Another example is Leena AI, which provides AI-powered virtual HR assistants to manage employee queries and engagement.
Mastercard partnered with Phenom to use AI-powered tools for creating a seamless recruitment experience. The company connected over 100 regional career sites to a talent CRM and automated interview scheduling with AI. This reduced scheduling time by 85% and led to over 5,000 interviews being booked within 24 hours. Mastercard boosted leads by 141,000 and increased conversion rates by 11%.
IT helpdesk
Conversational AI in an IT help desk automates routine support tasks like password resets, access requests, and troubleshooting common technical issues. Instead of navigating complex portals, employees can quickly chat with an AI assistant that understands their problem and offers step-by-step fixes.
This decreases the queue to your IT team and lets your employees solve issues on their own. Your IT support people will thank you for that.
One of the best providers for this is Moveworks. It’s an AI platform specializing in IT helpdesk automation that integrates with collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams to resolve employee IT issues instantly.
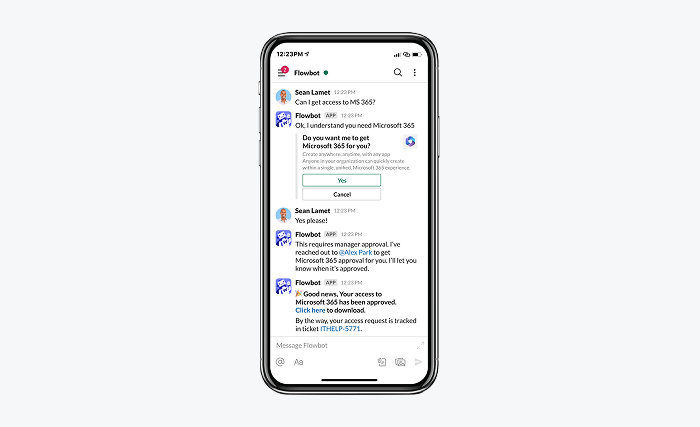
Webflow, a global leader in no-code web design, used AI to move from a managed service provider to an in-house support model. To ensure high-quality service for its remote workforce, the company integrated AI into its IT processes. As a result, AI now resolves 50% of IT issues and enables the IT team to focus on strategic initiatives.
Fintech
Conversational AI in fintech empowers banks and financial institutions to deliver efficient customer interactions. AI assistants can support tasks like answering account-related queries and guiding users through loan or mortgage applications. Moreover, the system can process payments and flag suspicious activity for your review.
With automation, financial services become more accessible and scalable without compromising compliance or security.
Kasisto (KAI) is a conversational AI platform built specifically for banking and financial services. It provides virtual assistants that handle digital banking tasks and maintain industry-grade security and compliance.
DBS Bank, a leading bank in Singapore, deployed virtual assistants to enhance its digital banking services. Customers can now ask about transactions, check balances, or get financial insights through natural conversations. And, as a result, DBS reported that millions of customer inquiries were successfully automated, which improved customer satisfaction across digital channels.

Conversational AI examples: key takeaway
From virtual assistants and CS chatbots to IT helpdesk solutions and fintech innovations, conversational AI tools bring speed and efficiency to everyday interactions. The beauty of this technology lies in its versatility: whether you’re streamlining HR processes or guiding shoppers through sales, it adapts to your needs and scales effortlessly.
If you’re ready to see these benefits in action, Lyro AI by Tidio is the perfect place to start.
Unlike generic chatbots, Lyro understands customer intent and learns over time. This system provides accurate answers instantly, resolving around 70% of customer inquiries without human involvement. As a result, your support will be faster and your customers happier.
Experience the power of conversational AI
FAQs
Tidio is a customer service and communication platform that combines live chat, chatbots, and AI tools to help businesses interact with customers in real time. It enables companies to automate responses and engage visitors directly on websites or through messaging apps.
Yes, Tidio uses AI to enhance customer support and sales through its virtual assistant called Lyro AI. Lyro can understand customer questions and provide relevant answers in natural language.
An example of conversational AI is Amazon Alexa, a virtual assistant that responds to voice commands. Users can ask Alexa to play music, control smart home devices, set reminders, and much more. It demonstrates how AI can understand natural language and perform tasks in everyday life.
The four types of AI are Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, and Self-Aware AI. Reactive Machines, like IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer, can analyze situations, but it doesn’t learn. Limited Memory AI, like self-driving cars, improves decisions by using past data. Theory of Mind AI (still in research) aims to understand human emotions and intentions. Self-Aware AI, which does not exist yet, would be conscious of itself and capable of independent thought.
John McCarthy is often called the “father of AI” for coining the term in 1956 and organizing the Dartmouth Conference that launched AI as an academic field of study. Some also credit Alan Turing, whose Turing Test laid the theoretical foundation for AI.

